Jan 31st 2024
Introduction to IIoT: Revolutionizing Industries with Smart Technology
In today's rapidly evolving technological landscape, the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) stands out as a transformative force in modern industries. This cutting-edge concept revolves around the seamless integration of machines, data, and human expertise to unlock unparalleled potential for information utilization.
This guide aims to demystify IIoT, offering an accessible yet insightful journey into its core meaning and workings. Whether you're a seasoned industry professional or new to the concept, this article will provide you with a foundational understanding of IIoT and its growing impact on the automation and control sectors - areas closely tied to the products and services offered by Electric Solenoid Valves.
Understanding IIoT – An Overview
What is IIoT and How Does it Work?

The Industrial Internet of Things, or IIoT, refers to the extension and use of the Internet of Things (IoT) in industrial sectors and applications. While IoT focuses on consumer devices and home automation, IIoT is specific to industrial settings, integrating machines and industrial equipment with networked sensors and software. This technology empowers industries to gather and analyze vital data, enabling enhanced performance, efficiency, and innovation.
At its core, IIoT is about connecting industrial equipment to the internet, allowing for real-time data collection, analysis, and exchange. This connectivity enables machines to communicate with each other and with human operators, leading to smarter, faster decision-making and more efficient industrial processes.
Key Components of IIoT
IIoT is comprised of several essential components that work in harmony:
- Sensors and Actuators: Embedded in machinery, these devices collect critical data on various parameters like temperature, pressure, and operation status, providing a comprehensive view of the industrial environment.
- Connectivity: Ensuring seamless data flow between devices and central systems, using technologies like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and cellular networks.
- Data Processing and Analytics: Advanced software and algorithms analyze the collected data to identify patterns, predict maintenance needs, and optimize operations.
- User Interface: IIoT systems feature user-friendly interfaces that allow human operators to interact effectively, monitor operations in real-time, and make informed, data-driven decisions, to maintain efficiency and minimize downtime.
Revolutionizing Industries:
By integrating these components, IIoT establishes intelligent networks that enable connected devices to autonomously monitor, collect, exchange, analyze, and respond to information without the need for constant human intervention. This remarkable capability drives efficiency, innovation, and growth in industrial environments, transforming the way industries operate and compete.
Differentiating IIoT from IoT
Understanding the Distinction between IoT and IIoT
While the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) and the Internet of Things (IoT) are closely related concepts, they cater to different applications and have distinct characteristics. Understanding this distinction is key to comprehending the full scope and potential of IIoT.
1. IoT: Connectivity in Daily Life
- Focus: IoT primarily focuses on consumer applications. This includes smart home devices like thermostats, refrigerators, and wearable technology.
- Objective: The main goal is to enhance convenience, comfort, and efficiency in daily life through interconnected devices.
- Data Volume and Security: IoT devices typically deal with less critical data. While security is important, a breach is less catastrophic than in industrial applications.
2. IIoT: Revolutionizing Industries
- Focus: IIoT is centered around industrial applications. This encompasses manufacturing equipment, supply chain monitoring systems, and large-scale industrial machines.
- Objective: The primary aim is to improve operational efficiency, safety, and decision-making in industrial settings. IIoT achieves this through real-time data monitoring, predictive maintenance, and automation.
- Data Volume and Security: IIoT deals with large volumes of data and requires robust security measures. The data is often critical to operations, and any breach can lead to significant safety risks and financial losses.
Key Differences:
- Scale and Complexity: IIoT operates on a much larger scale and involves more complex systems compared to typical IoT setups.
- Reliability and Precision: IIoT requires higher reliability and precision. Industrial processes depend on accurate and consistent data for smooth operation.
- Integration with Industrial Processes: IIoT is deeply integrated with core industrial processes, whereas IoT tends to be more supplementary in nature.
While IoT enhances everyday life, IIoT drives industrial innovation and efficiency. Both play pivotal roles in their respective domains, but the stakes, scale, and complexity are significantly higher in IIoT, making it a critical component in the future of industrial automation and smart manufacturing.
Real-World Applications and Examples of IIoT
Exploring the Impact of IIoT Across Industries

The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is not just a theoretical concept; it's a practical innovation driving significant changes across various industries. By examining real-world applications, we can better understand the transformative power of IIoT.
1. Manufacturing: Smart Factories
- Application: In manufacturing, IIoT is used to create 'smart factories' where machinery and equipment are interconnected and communicate continuously. This connectivity allows for real-time monitoring and adjustment of manufacturing processes.
- Example: A car manufacturing plant uses IIoT to monitor assembly line operations, with sensors providing data on machine performance and product quality. This leads to reduced downtime and enhanced quality control.
2. Healthcare: Enhanced Patient Care
- Application: IIoT plays a vital role in healthcare by enabling remote monitoring of patient health and automating various medical processes.
- Example: Hospitals use IIoT devices to track patients’ vital signs in real-time, allowing for prompt medical intervention when necessary.
3. Agriculture: Precision Farming
- Application: In agriculture, IIoT aids in precision farming, where sensors collect data on soil conditions, crop growth, and weather patterns, leading to more informed decisions.
- Example: A farm employs IIoT sensors to monitor soil moisture and nutrient levels, adjusting irrigation and fertilization automatically for optimal crop growth.
4. Energy: Smart Grid Management
- Application:The energy sector utilizes IIoT for smart grid management, optimizing energy distribution and consumption.
- Example: An electric utility company integrates IIoT into its grid to monitor and balance energy loads, improving efficiency and reducing outages.
5. Logistics: Supply Chain Optimization
- Application: IIoT enhances supply chain transparency and efficiency by tracking goods from manufacturing to delivery.
- Example: A logistics company uses IIoT-enabled devices to track shipments in real-time, ensuring timely delivery and inventory management.
These examples illustrate just a few ways IIoT is revolutionizing industries by providing more data-driven insights, automating processes, and enhancing efficiency. As industries continue to evolve, IIoT will play an increasingly vital role in shaping the future of industrial operations.
IIoT Technologies
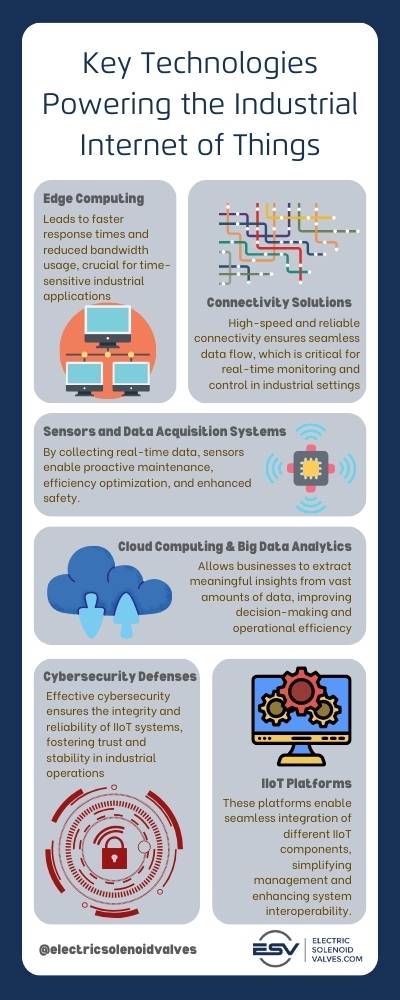
Key Technologies Powering the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is powered by a range of advanced technologies. Understanding these technologies provides insights into how IIoT achieves its incredible capabilities of automation, data analysis, and connectivity.
1. Sensors and Data Acquisition Systems
- Role: Sensors are the eyes and ears of IIoT, gathering crucial data from machines and environments. This data can include temperature, pressure, humidity, and operational metrics.
- Impact: By collecting real-time data, sensors enable proactive maintenance, efficiency optimization, and enhanced safety.
2. Connectivity Solutions
- Role: Robust connectivity is essential for transmitting data from sensors to processing systems. Technologies like Wi-Fi, 5G, and Low Power Wide Area Networks (LPWAN) play a crucial role.
- Impact: High-speed and reliable connectivity ensures seamless data flow, which is critical for real-time monitoring and control in industrial settings.
3. Edge Computing
- Role: Edge computing involves processing data near its source, reducing the need for data to travel to centralized data centers.
- Impact: This leads to faster response times and reduced bandwidth usage, crucial for time-sensitive industrial applications.
4. Cloud Computing and Big Data Analytics
- Role: Cloud platforms offer scalable storage and powerful computing capabilities, enabling advanced data analytics.
- Impact: Big data analytics allows businesses to extract meaningful insights from vast amounts of data, improving decision-making and operational efficiency.
5. Cybersecurity Measures
- Role: As IIoT systems handle sensitive and critical data, robust cybersecurity measures are imperative to protect against breaches and attacks.
- Impact: Effective cybersecurity ensures the integrity and reliability of IIoT systems, fostering trust and stability in industrial operations.
6. IIoT Platforms
- Role: IIoT platforms are integrated suites of hardware and software that manage and analyze data from IIoT devices. They act as the central hub for IIoT systems.
- Impact: These platforms enable seamless integration of different IIoT components, simplifying management and enhancing system interoperability.
Through these technologies, IIoT transcends traditional industrial limitations, ushering in a new era of efficiency, productivity, and innovation. As these technologies continue to evolve, they will further empower industries to meet the challenges of a rapidly changing world.
Benefits and Goals of IIoT
Harnessing IIoT for Enhanced Industrial Performance
The adoption of the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) introduces a plethora of advantages that revolutionize industrial operations. Understanding these benefits, alongside the overarching goals of IIoT, helps in appreciating its full potential and the reasons behind its rapid adoption across various sectors.
1. Enhanced Operational Efficiency
- Benefit: IIoT systems leverage real-time data analysis to optimize operations, leading to reduced downtime and increased productivity.
- Goal: The primary goal is to streamline industrial processes, reducing waste and enhancing the quality of output.
2. Improved Safety and Compliance
- Benefit: Through continuous monitoring and predictive maintenance, IIoT significantly improves workplace safety and ensures compliance with regulatory standards.
- Goal: The aim is to create a safer working environment, reducing the likelihood of accidents and violations.
3. Predictive Maintenance
- Benefit: IIoT enables proactive maintenance by identifying potential equipment failures before they occur, reducing unexpected downtimes.
- Goal: To transition from reactive to proactive maintenance strategies, saving time and resources.
4. Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
- Benefit: By monitoring and optimizing energy usage, IIoT contributes to greater energy efficiency and reduced environmental impact.
- Goal: To promote sustainable industrial practices through efficient utilization of resources.
5. Enhanced Product Quality
- Benefit: Continuous monitoring and control over production processes result in higher quality products and fewer defects.
- Goal: To consistently meet and exceed quality standards, enhancing customer satisfaction.
6. Better Decision-Making
- Benefit: The wealth of data provided by IIoT helps support more informed decision-making, allowing businesses to respond faster to market changes and opportunities.
- Goal: To enable data-driven decision-making, fostering agility and competitiveness.
7. Customization and Innovation
- Benefit: IIoT opens avenues for customizing production processes and developing innovative products and services.
- Goal: To drive innovation and meet specific customer needs through flexible and adaptive processes.
The benefits and goals of IIoT revolve around enhancing efficiency, safety, quality, and sustainability in industrial operations. As technology continues to evolve, IIoT will play an increasingly pivotal role in shaping the future of industries, enabling them to become more responsive, efficient, and adaptable to changing demands.
Conclusion: Embracing the IIoT Revolution
As we've explored throughout this guide, the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is not just a futuristic concept, but a present-day reality with profound impacts across numerous industries. From enhancing operational efficiency to driving innovation, IIoT is reshaping the industrial landscape, offering transformative solutions to longstanding challenges.
The intricate ecosystem of IIoT, comprising cutting-edge technologies, diverse applications, and numerous benefits, showcases the power of interconnectedness and intelligent data analysis. As industries continue to evolve and embrace Industry 4.0, IIoT will play a pivotal role in shaping the future of industrial automation and smart manufacturing. By leveraging the key technologies that power IIoT, businesses can gain invaluable insights, automate processes, and achieve unprecedented levels of efficiency and productivity.
For professionals and businesses in the realms of automation and control, like those associated with Electric Solenoid Valves, the opportunities presented by IIoT are vast. By capitalizing on the power of IIoT, they can not only streamline their current operations but also lay the groundwork for new innovations and advancements.
As technology continues to evolve, the significance of IIoT will only grow, making it an indispensable part of the industrial world. By harnessing the power of the Industrial Internet of Things, industries can unlock a world of possibilities, driving growth, competitiveness, and sustainability in the years to come. The journey towards Industry 4.0 begins with IIoT, and it's an opportunity that forward-thinking businesses cannot afford to miss.