Posted by Electric Solenoid Valves on Feb 11th 2026
NPT vs BSP Threads: Key Differences, Sealing Methods, and Why They Matter
Confusion around NPT vs BSP threads is one of the most common causes of leaks, damaged ports, and installation failures in solenoid valve systems. Although NPT and BSP threads may look similar at first glance, they are not interchangeable. Using the wrong thread standard can lead to poor sealing, cracked valve bodies, and premature valve failure.
Because solenoid valves rely on proper mechanical sealing at the port connection, understanding thread type is critical. In this guide, we explain the difference between NPT vs BSP threads, how each seals, and why correct thread selection matters when specifying solenoid valves.
Why Thread Standards Matter in Solenoid Valve Applications
Thread type directly affects how a valve seals into a piping system. Unlike flanged or compression fittings, pipe threads either seal through thread interference or with a secondary sealing surface such as an O-ring or washer.
When the wrong thread standard is used, several problems appear quickly. For example, leaks may persist even after applying additional sealant. In addition, fittings may feel tight while sealing poorly. Over time, excessive tightening can crack brass, stainless, or plastic valve bodies.
As a result, many issues that appear to be valve defects are actually installation problems caused by mismatched threads. This is why thread compatibility should always be confirmed before ordering or installing a solenoid valve.
What Is NPT?
NPT stands for National Pipe Thread. It is the most common pipe thread standard used in North America and is widely found in plumbing, industrial, HVAC, and process control systems.
Key Characteristics of NPT Threads
- Tapered thread design
- Thread angle of 60 degrees
- Seals through metal to metal interference
- Requires thread sealant such as PTFE tape or pipe dope
- Nominal size does not match the measured diameter
Because NPT threads taper, the male and female threads wedge together as they tighten. Therefore, sealing occurs as the threads deform slightly and sealant fills the remaining gaps.
For this reason, NPT threads must never be installed dry. Without sealant, leakage is likely even if the connection feels tight.
How NPT Threads Seal
NPT threads rely on friction and deformation to create a seal. As tightening increases, contact pressure rises along the thread flanks. However, microscopic gaps still exist between threads.
Thread sealant plays a critical role. It fills these gaps, reduces galling, and allows proper torque without damaging the valve body. Because of this, overtightening an NPT connection to stop a leak is a common mistake.
In solenoid valve installations, overtightening often damages the port before sealing improves.
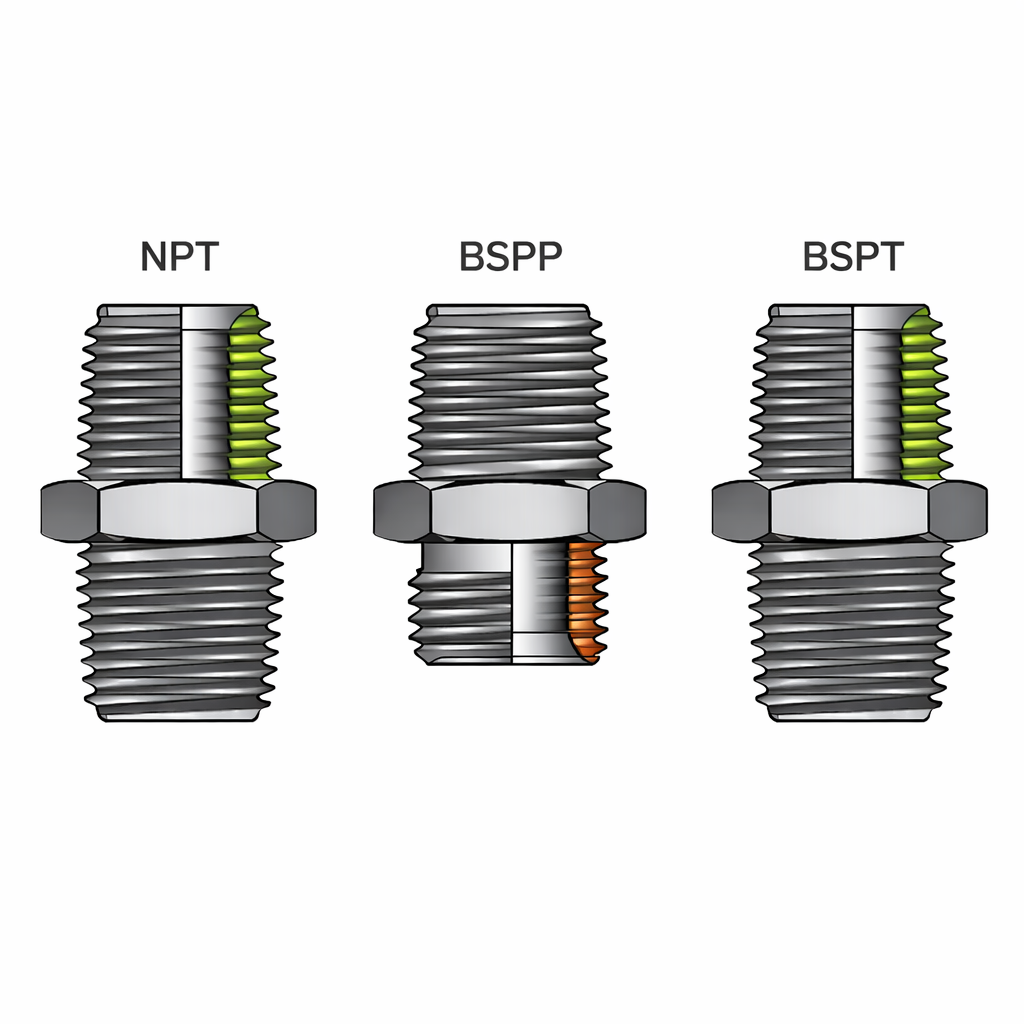
What Is BSP?
BSP stands for British Standard Pipe. It is commonly used in Europe, Asia, Australia, and many globally manufactured systems. Unlike NPT, BSP includes two distinct thread forms.
Understanding which BSP type is present is essential when comparing NPT vs BSP threads.
BSPP vs BSPT Explained
BSPP, British Standard Pipe Parallel
- Parallel thread, no taper
- Thread angle of 55 degrees
- Does not seal on the threads
- Requires an O-ring, bonded seal, or washer
Because BSPP threads are straight, tightening alone does not create a seal. Instead, sealing occurs at the face of the fitting. Therefore, BSPP connections should never rely on thread sealant as the primary sealing method.
BSPT, British Standard Pipe Tapered
- Tapered thread
- Thread angle of 55 degrees
- Seals by thread interference and sealant
- Similar concept to NPT, but not compatible
Although BSPT and NPT are both tapered, they differ in thread angle and pitch. As a result, BSPT and NPT threads will not seal reliably together.
NPT vs BSP Threads: Technical Differences
|
Feature |
NPT |
BSP |
|
Thread angle |
60 degrees |
55 degrees |
|
Taper |
Yes |
BSPT only |
|
Sealing method |
Thread interference + sealant |
O-ring, washer, or taper |
|
Common regions |
North America |
Europe, Asia, Australia |
|
Interchangeable |
No |
No |
In contrast to visual similarity, these differences prevent proper sealing. Even minor mismatches in angle and pitch create uneven stress and leakage paths.
Why NPT vs BSP Threads Are Not Interchangeable
A common assumption is that BSP fittings can be used in NPT ports with enough tape. However, this approach creates more problems than it solves.
When comparing NPT vs BSP, the mismatch causes:
- Uneven thread contact
- High localized stress
- Poor long-term sealing
- Increased risk of cracked ports
Initially, the connection may appear secure. Over time, vibration, pressure cycling, or temperature changes worsen the seal. Eventually, leaks or mechanical damage occur.
This is especially problematic in solenoid valves, where internal alignment is critical for reliable operation.
How Thread Mismatch Affects Solenoid Valve Performance
Thread issues affect more than just leakage. They also influence valve reliability and service life.
Incorrect thread engagement can:
- Distort valve ports
- Create internal stress fractures
- Make future removal difficult
- Reduce sealing reliability under pressure
Because solenoid valves contain moving internal components, any mechanical distortion of the valve body increases the risk of sticking or inconsistent operation.
Therefore, thread compatibility is part of overall valve performance, not just installation convenience.
Why Most ElectricSolenoidValves.com Valves Use NPT
At ElectricSolenoidValves.com, most valves are supplied with NPT ports. This matches North American standards and simplifies sourcing fittings, manifolds, and accessories.
In addition, NPT ports align with:
- Common plumbing hardware
- Industrial control panels
- Typical OEM and retrofit systems
For international applications, adapters can be used to convert NPT to BSPP or BSPT—but adapters must be chosen carefully to ensure proper sealing on both sides. Re‑tapping valve ports is never recommended, as it removes material, alters pressure ratings, and voids warranties.
Identifying Your Existing Thread Type
If you are unsure which thread standard your system uses, do not guess. Instead, follow a structured approach.
Steps to identify thread type:
- Review equipment or valve datasheets
- Measure thread pitch with a gauge
- Check for O-rings or sealing washers
- Observe whether the thread tapers
- Consider the origin of the equipment
In many cases, imported machinery uses BSP threads, even when installed in North American facilities.
Common Applications Where BSP Threads Appear
BSP threads are frequently found in:
- Imported pneumatic equipment
- European hydraulic systems
- OEM assemblies designed for global markets
- Equipment manufactured outside North America
In these cases, specifying an NPT solenoid valve without proper adaptation leads to persistent sealing problems.
Adapters vs Re-Tapping Valve Ports
Adapters are acceptable when converting between thread standards. Re-tapping valve ports is not recommended.
Re-tapping:
- Removes critical material
- Alters pressure ratings
- Increases cracking risk
- Voids warranties
Adapters preserve the original port geometry and allow correct sealing on both interfaces.
Best Practices When Choosing Between NPT vs BSP
Before selecting a solenoid valve:
- Confirm thread type on piping and valves
- Verify the sealing method
- Match thread standards intentionally
- Use adapters when needed
- Avoid forcing mismatched threads
As a result, installation becomes easier, sealing improves, and valve life increases.
Final Thoughts on NPT vs BSP Threads
The difference between NPT and BSP threads may seem minor, but it has a major impact on sealing, reliability, and valve lifespan. These standards are not interchangeable, and forcing compatibility often leads to leaks and damage.
By understanding thread types upfront, you prevent installation issues and protect both the valve and the system.
Need help confirming thread compatibility for your solenoid valve application?
Contact our team today:
> 800‑983‑8230

